Introduction
LoRaWAN (Long Range modulation Wide Area Network) is the fusion of LoRa (Long Range modulation) and LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) and it has the data transference between devices with low data rate and the advantages of a large range and low power consumption. We do not have to confuse it with LoRa! LoRa is the type of modulation in the communication and LoRaWAN is a protocol applied above LoRa. If we compare them with OSI layer model: LoRa is in the Physical Layer whereas LoRaWAN is located between Presentation, Session and Transport Layers.
Related links
Most used communications in each Industry Sector
Read >>
How to use communication protocols in industrial automation
Read >>
What is LoRa?
Read >>
LoRa industrial PLC controller Family
Read >>
How to work with LoRa WAN?
Read >>
Main characteristics:
Star structured network
Large range (10 - 15 km in line of sight)
Secure method: AES-128 Encryptation
3 different node types supported
Devices management
Public and private networks
Low consumption
Low data transference (until 242 bytes)
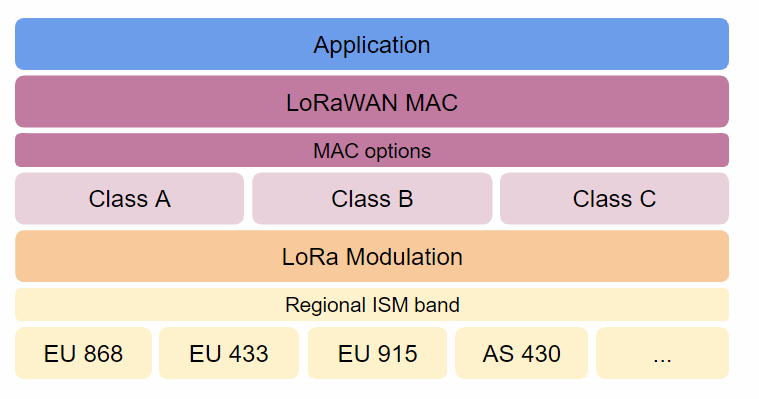
Node classes:
Class A: This is the most used by all the devices and offers the lowest consumption because, after the data is sent to the gateway, it starts the Rx windows (only listening mode). It is a perfect choice for devices that uses batteries.
Class B: This kind has the reception windows fixed by periods of time determined by the gateway. It can be used by devices powered by batteries or connected to the electrical network, depending on the listening time periods.
Class C: This type has the highest consumption so it is always in the listening mode and, only when it is needed, in transmit mode. It is recommended to use this one with devices powered by the electrical network or an external power supply.
Common applications:
P2P (point-to-point) connections, in other words, connections between two different devices.
Sensors and actuators networks located where it is needed (cities, industries, countryside, etc.)
IoT networks that can work with low data rates. This means that things like the transference of voice or video will be very slow or impossible.
Provide service in zones where other kinds of technologies like the cellular one (3G, 4G, 5G...) cannot cover, thanks to its wide range of action.
Here we can see an example of a LoRaWAN network:
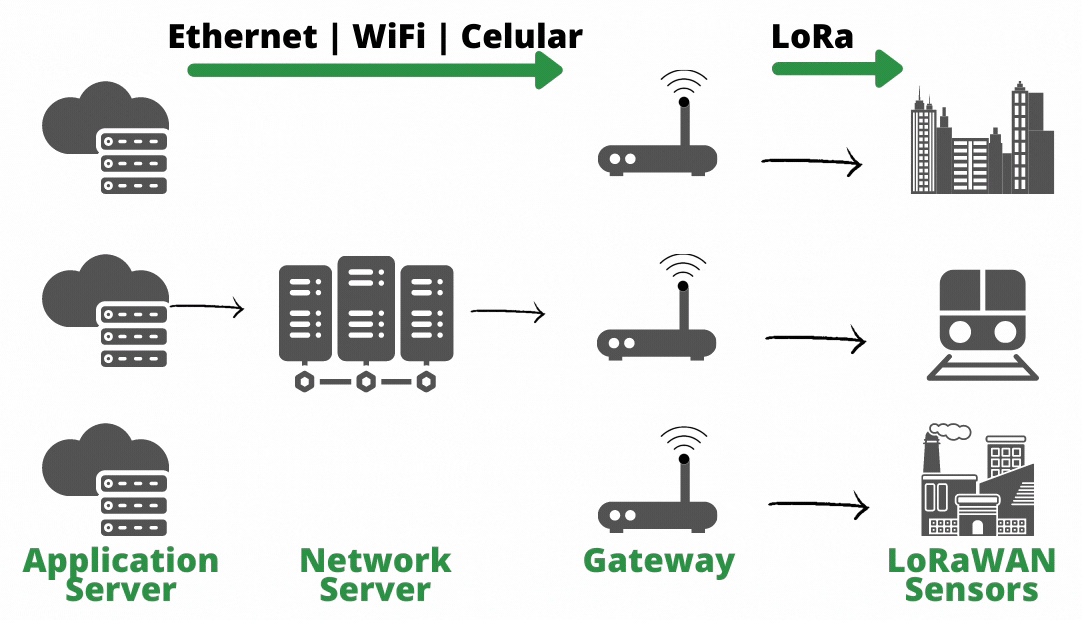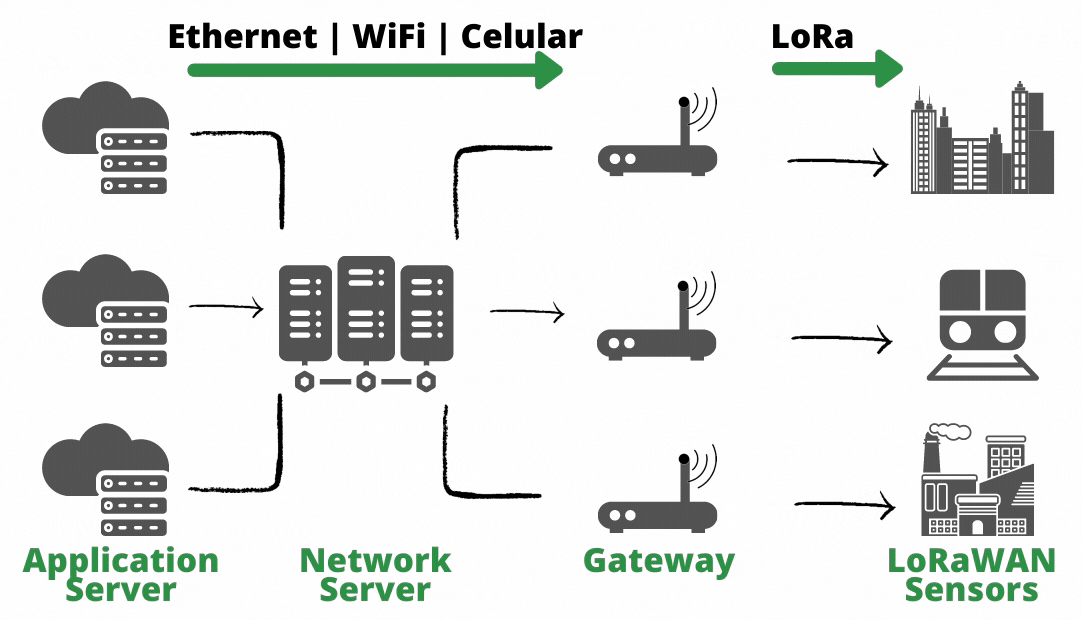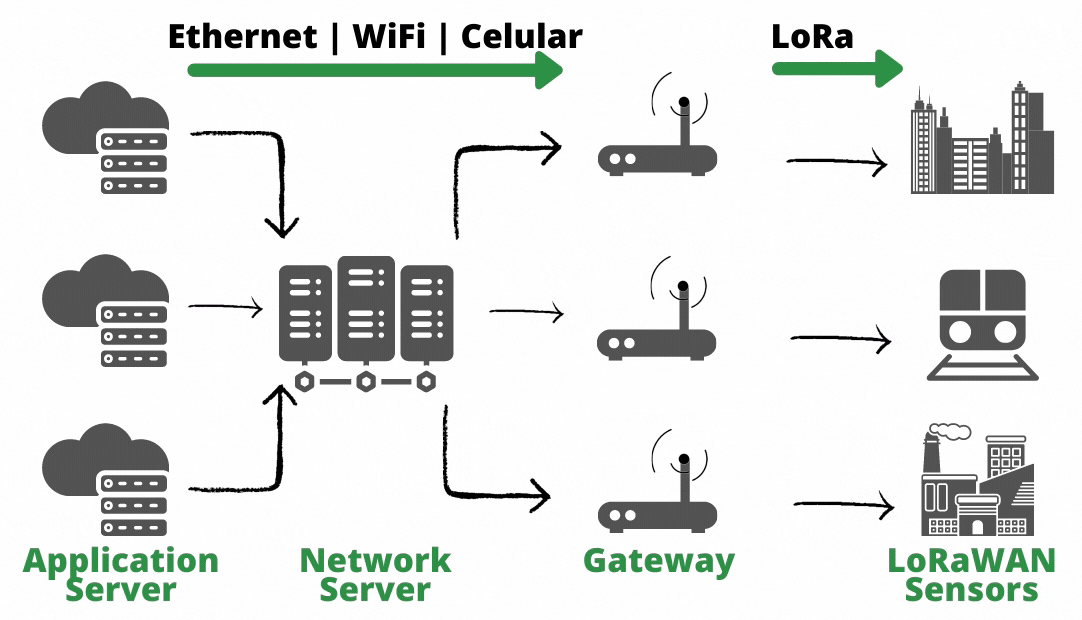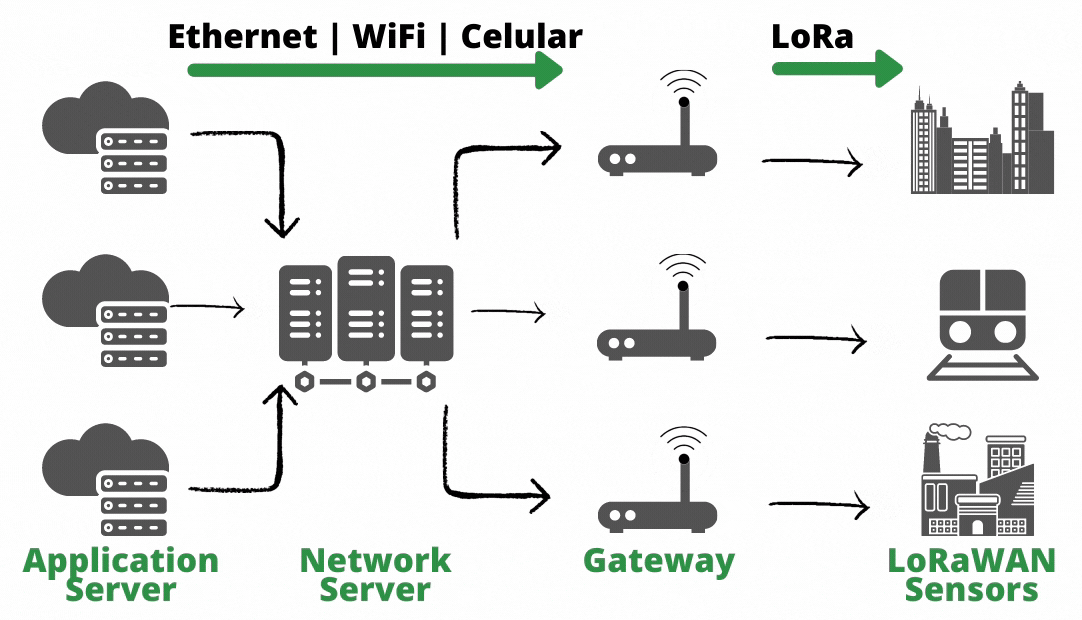
What is LoRaWAN?