Initial Installation
ARDUINO IDE
Arduino IDE is the Original platform to program Arduino boards. This cross-platform application is available on Windows, macOS and Linux and under the GNU General Public License.
Arduino IDE supports C and C++ code structuring. Industrial Shields recommend using Arduino IDE to program Arduino Based PLC’s, but any Arduino compatible software are compatible with Industrial Shields Controllers.
Apart from that, Industrial Shields bring the possibility to select your Arduino based PLC into your Arduino IDE and compile your sketches for the different PLC’s.
Download the Arduino IDE 1.8.6:
Inputs & Outputs
ANALOG INPUTS
Voltage variation between –Vcc (or GND) and +Vcc, can take any value. An analog input provides a coded measurement in the form of a digital value with an N-bit number. In Digital and Analog I/O there’s self insulation, so its posible to connect them in a different power supply than 24 V.
Inputs: (16x) Analog Inputs (0-10Vdc) / Digital (7-24Vdc) configurable
by software.
To know more about analog inputs...
TYPICAL CONNECTION
DIGITAL INPUTS
Voltage variation from –Vcc (or GND) to +Vcc, with no intermediate values. Two states: 0 (-Vcc or GND) and 1 (+Vcc). In Digital and Analog I/O there’s self insulation, so its posible to connect them in a different power supply than 24 V.
Inputs: (16x) Analog Inputs (0-10Vdc) / Digital (7-24Vdc) configurable by software.
(20x) Isolated Digital (7-24Vdc).
To know more about digital inputs...
TYPICAL CONNECTION
- Digital Isolated Input
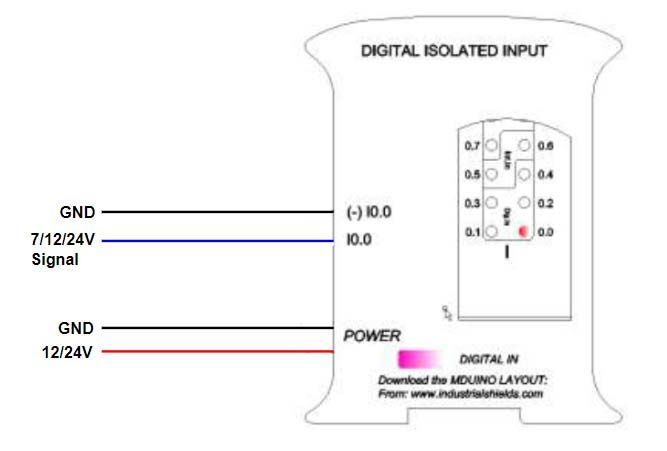
- Digital No Isolated Input
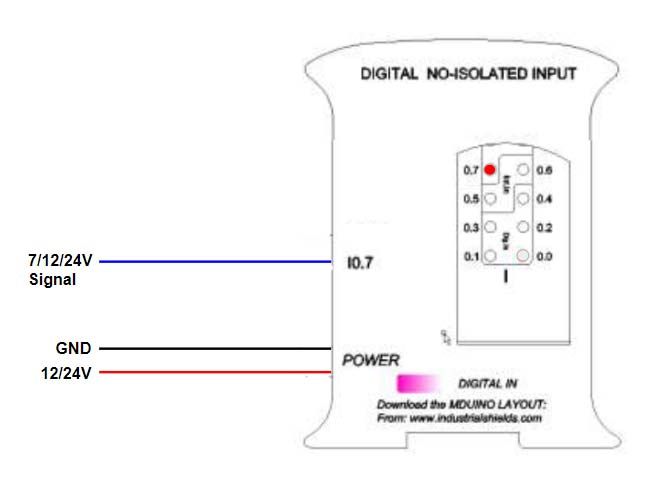
INTERRUPT INPUTS
Interrupt Service Rutine. A mechanism that allows a function to be associated with the occurance of a particular event. When the event occurs the processor exits immediately from the normal flow of the program and runs the associated ISR function ignoring any other task.
| Interrupt | Arduino Mega Pin | M-Duino Pin |
| INT0 | 2 | I0.5/INT0 |
| INT1 | 3 | I0.6/INT1 |
| INT4 | 19 | I1.6/INT4 |
| INT5 | 18 | I1.5/INT5 |
| INT2 | 21 | I2.6/INT2 |
| INT3 | 20 | I2.5/INT3 |
- I0.5/INT0 and I0.6/INT1 also as Pin3 and Pin2. Enable Interrupts turning ON the switches number 3 and 4 of down communication switches.
- I1.5/INT4 and I1.6/INT5 also as Tx1 and Rx1. Enable Interrupts turning ON the switches number 1 and 2 of up communication switches.
- I2.5/INT3 and I2.6/INT2 also as SCA and SCL. Enable Interrupts turning ON the switches number 3 and 4 of up communication switches. In this case you won’t be able to use I2C.
To know more about interrupt inputs...
TYPICAL CONNECTION
Code example
In this example we activate INT0 using pin I0_5 from M-duino board. When there’s a change
#define INTERRUPT I0_5 //other pins: I0_6, I2_6, I2_5, I1_6, I1_5 (M-Duino) I0_0, I0_3, I0_2, I0_1 (Ardbox)
volatile bool state = false;
void setup() {
pinMode(INTERRUPT, INPUT_PULLUP);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(INTERRUPT), function_call_back, CHANGE);
}
void loop() {
if (state == true){
Serial.println("Interrupt activated");
state = false;
}
}
void function_call_back(){ //Change led state
state = true;
}
Communications
Ethernet
Ethernet is the technology that is most commonly used in wired local area networks ( LANs ).
A LAN is a network of computers
and other electronic devices that covers a small area such as a room, office, or building. It is used in contrast to a wide area
network (WAN) , which spans much larger geographical areas.
Ethernet is a network protocol that controls how data is
transmitted over a LAN. Technically it is referred to as the IEEE 802.3 protocol. The protocol has evolved and improved over time
to transfer data at the speed of a gigabit per second.
Our M-Duino family incorporate the integrated W5500 IC.
WX5500 is a Hardwired TCP/IP embedded Ethernet controller that provides easier Internet connection to embedded systems. This chip enables users to have Internet connectivity in their applications by using the single chip in which TCP/IP stack, 10/100
Ethernet MAC and PHY are embedded. The W5500 chip embeds the 32Kb internal memory buffer for the Ethernet packet
processing. With this chip users can implement the Ethernet application by adding the simple socket program. SPI is provided for
easy integration with the external microcontroller.
Hardware
Hardware configuration
*IMPORTANT: Make sure that your Ethernet PLC is powered (12-24Vdc). Just with USB is insufficient power to power up the
Ethernet communication.
Switch configuration
For the Ethernet communication protocol there isn’t any switch that affects it. So it does not matter the configuration of the
switches to implement Ethernet communication.
Used pins
For Ethernet communication protocol, the defined Arduino Mega pin is pin 10 , which is connected and already internally
assembled to the WX5500 Ethernet controller. W5500 IC communicates to the Mega board via SPI bus already assembled too.
You can
access easily to Ethernet port in our Ethernet PLCs, it is located at the top of the communications layer.
Ethernet hardware configuration must be plug and play.
Software
*IMPORTANT: Make sure to download the Arduino based PLC boards for Arduino IDE.
Software Configuration:
Once the hardware configuration is done, it is possible to proceed with the software configuration and also its usage. Firstable it is necessary to include
the Ethernet2.h library provided by Industrial Shields (has the same functionallity as Ethernet.h and also
the same usage).
#include <Ethernet2.h> * Remember that for the V7 version or earlier versions you must use the <Ethernet.h> library.Ethernet2 Library - functions.
* Ethernet2.h library has the same functions as Ethernet.h.
Example Codes:
Echo TCP Server:
Once the server is running, any client can connect to the server. On this example it is used an M-Duino to generate the server. The
example of TCP client showed before could be one of the clients.
Next it is showed the Arduino IDE code:
// use Ethernet.h if you have a M-Duino V7 version
#include <Ethernet2.h>
// mac address for M-Duino
byte mac[] = { 0xBE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED };
// Ip address for M-Duino
byte ip[] = { 192, 168, 1, 100 };
int tcp_port = 5566;
EthernetServer server = EthernetServer(5566);
void setup()
{
// initialize the ethernet device
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip);
// start server for listenign for clients
server.begin();
}
void loop()
{
// if an incoming client connects, there will be bytes available to read:
EthernetClient client = server.available();
if (client.available()) {
// read bytes from the incoming client and write them back
// to the same client connected to the server
client.write(client.read());
}
}
Echo TCP Client:
Once the server is running, M-Duino can connect to the server. On this example it is used an M-Duino to connect with the Node.js
server called server.js, the same as used on previous example link.
To configure the M-Duino, this post just follows the TCP example from Arduino web site with a few changes. To be able to connect to the server we must know the TCP server IP and the port where this server is listening.
Next it is showed the Arduino code:
#include <Ethernet2.h>
#include <SPI.h>
byte mac[] = { 0xBE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED };
byte ip[] = { 192, 168, 1, 100 };
byte server[] = { 192, 168, 1, 105 }; // Touchberry Pi Server
int tcp_port = 5566;
EthernetClient client;
void setup()
{
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip);
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(1000);
Serial.println("Connecting...");
if (client.connect(server, tcp_port)) { // Connection to server.js
Serial.println("Connected to server.js");
client.println();
} else {
Serial.println("connection failed");
}
}
void loop()
{
if (client.available()) {
if(Serial.available()){
char s = Serial.read();
client.write(s); // Send what is reed on serial monitor
char c = client.read();
Serial.print(c); // Print on serial monitor the data from server
}
}
if (!client.connected()) {
Serial.println();
Serial.println("disconnecting.");
client.stop();
for(;;) ;
}
}To know more about Ethernet communication...
Ethernet with HTTP.
Ethernet with MQTT.
Ethernet with Modbus TCP/IP (PLC = Slave).
Ethernet with Modbus TCP/IP (PLC = Master).
Serial TTL
Communication Interface between two devices with a low level voltage. A Serial port sends data by a bit sequence.
Two signals: Tx (Transmit Data) and Rx (Receive Data).
M-Duino has two TTL ports, RX0/TX0, RX1/TX1. TTL0 is accessed with the function Serial (pins 0 and 1 of the Arduino Mega). TTL1 is accessed with the function Serial1 (pins 18 and 19 of the Arduino Mega).
To know more about Serial TTL...
Hardware
IMPORTANT: Make sure that your Ethernet PLC is powered (12-24Vdc).
Switch configuration
To achieve Serial TTL communication there isn't any switch that affects it, it is always enabled. So it does not matter the configuration of the switches to implement Serial TTL communication.
Used pins
| MDuino Ethernet PLC Pinout | Arduino Mega Pinout |
| Tx 0 | 0 |
| Rx 0 | 1 |
| Tx 1 | 18 |
| Rx 1 | 19 |
Software
IMPORTANT: Make sure to download the Arduino based PLC boards for Arduino IDE.
Software Configuration
Once the hardware configuration is done, it's possible to proceed with the software configuration and also its usage. Firstable it's necessary to include the RS232.h library provided in our boards. Then don’t forget to implement the proper initialization of your communication on the setup() function:
Serial.begin(9600);
Basic Serial TTL write example
Reads an analog input on Tx0 (pin 0), prints the result to the serial monitor.
Graphical representation is available using serial plotter (Tools > Serial Plotter menu) on Arduino IDE serial monitor.
// the setup routine runs once when you press reset:
void setup() {
pinMode(I0_2, INPUT);
// initialize serial communication at 9600 bits per second:
Serial.begin(9600);
}
// the loop routine runs over and over again forever:
void loop() {
// read the input on analog pin 0:
int sensorValue = analogRead(I0_2);
// print out the value you read:
Serial.println(sensorValue);
delay(1); // delay in between reads for stability
}
I2C
I2C is a synchronous protocol. Only uses 2 cables, one for the clock (SCL) and one for the data (SDA). This means that the master and the slave send data through the same cable, which is controlled by the master, who creates the clock signal. I2C does not use slave selection, but addressing.
I2C is a serial communications bus. The speed is 100 kbit/s in standard mode, but also allows speeds of 3.4 Mbit/s. It is a bus very used in the industry, mainly to communicate microcontrollers and their peripherals in integrated systems and generalizing more to communicate integrated circuits among themselves that normally reside in a same printed circuit.
Hardware
IMPORTANT: Make sure that your Ethernet PLC is powered (12-24Vdc).
Switch configuration
To achieve I2C communication there isn't any switch that affects it, it is always enabled. So it does not matter the configuration of the switches to implement I2C communication.
Used pins
| MDuino Ethernet PLC Pinout | Arduino Mega Pinout |
| SDA | 20 |
| SCL | 21 |
Software
SPI
These pins can only work as a 5V pins if the Ethernet protocol is not going to be used. As the Ethernet protocol uses the SPI to communicate with the Arduino board, both behaviours cannot happen at the same time as the Ethernet would not work.
These pins are not stablished with a pull-up or a pull-down configuration. The state of thesepins is unknown. If these pins must be used, they require a pull-up or a pull-downconfiguration. The Arduino board allows the pins to be set in a pull-up configuration. If not itmust be stablished an external pull-up or pull-down circuit in order to correctly work with these pins.
Hardware
IMPORTANT: Make sure that your Ethernet PLC is powered (12-24Vdc).
Switch configuration
To achieve SPI communication there isn't any switch that affects it, it is always enabled. So it does not matter the configuration of the switches to implement SPI communication.
Used pins
For Serial communication protocol the defined Arduino Mega pins are showed in the chart below. For SPI bus MISO, MOSI and CLOCK pins are
common to all the connected devices to the M-Duino, conversely, each of the connected devices will have a single and dedicated SS pin.
| Function | M-Duino connection | Arduino Mega Pinout |
| MISO | SO | 50 |
| MOSI | SI | 51 |
| CLOCK | SCK | 52 |
| RST | Reset | Reset |
IMPORTANT: Make sure to download the Arduino based PLC boards for Arduino IDE.
// inslude the SPI library:
#include <SPI.h>
// set pin 10 as the slave select for the digital pot:
const int slaveSelectPin = 10;
void setup() {
// set the slaveSelectPin as an output:
pinMode(slaveSelectPin, OUTPUT);
// initialize SPI:
SPI.begin();
}
void loop() {
// go through the six channels of the digital pot:
for (int channel = 0; channel < 6; channel++) {
// change the resistance on this channel from min to max:
for (int level = 0; level < 255; level++) {
digitalPotWrite(channel, level);
delay(10);
}
// wait a second at the top:
delay(100);
// change the resistance on this channel from max to min:
for (int level = 0; level < 255; level++) {
digitalPotWrite(channel, 255 - level);
delay(10);
}
}
}
void digitalPotWrite(int address, int value) {
// take the SS pin low to select the chip:
digitalWrite(slaveSelectPin, LOW);
// send in the address and value via SPI:
SPI.transfer(address);
SPI.transfer(value);
// take the SS pin high to de-select the chip:
digitalWrite(slaveSelectPin, HIGH);
}
Special Functions
RTC
The term real-time clock is used to avoid confusion with ordinary hardware clocks which are only signals that govern digital electronics, and do not count time in human units. RTC should not be confused with real-time computing, which shares the acronym but does not directly relate to time of day.
Although keeping time can be done without an RTC, using one has benefits:
- Low power consumption (important when running from alternate power
- Frees the main system for time-critical tasks
- Sometimes more accurate than other methods
There is a 3,3V lithium coin cell battery supplying the RTC. M-Duinos RTC Module is based on the DS1307 Chip . The DS1307 serial real-time clock (RTC) is a lowpower, full binary-coded decimal (BCD) clock/calendar plus 56 bytes of NV SRAM. Address and data are transferred serially through an I2C , bidirectional bus. The clock/calendar provides seconds, minutes, hours, day, date, month, and year information. The end of the month date is automatically adjusted for months with fewer than 31 days, including corrections for leap year. The clock operates in either the 24-hour or 12-hour format with AM/PM indicator. The DS1307 has a built-in power-sense circuit that detects power failures and automatically switches to the backup supply. Timekeeping operation continues while the part operates from the backup supply.
Hardware Configuration
IMPORTANT: Make sure that your Ethernet PLC is powered (12-24Vdc) .
Switch configuration
RTC works with the I2C protocol communication, so it is required to have enabled the I2C protocol.
4 switches have to be configured in order to enable the RTC features and I2C communication:
| SWITCH | ON | OFF |
| NC | - | - |
| NC | - | - |
| RTC/SCL | RTC | - |
| RTC/SDA | RTC | - |
RTC SCL & RTC SDA must be set to ON mode to enable the I2C wires to the RTC. If they are in OFF mode, the Arduino won’t communicate with the RTC.
Software Configuration
Once the hardware configuration is done, it's possible to proceed with the software configuration and also its usage. Firstable it's necessary to include the RTC.h library provided in our boards (RTC.h includes I2C.h initialitzation, so it will not be necessary to initialize the I2C.h library):
#include <RTC.h>
To check if the RTC port is working it is easy to use the serial monitor from the Arduino IDE using the right sentence inside the setup() function:
#Serial.begin(9600L)
Example Code
Basic RTC Test
// RTC library example
// by Industrial Shields
#include <RTC.h>
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600L);
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void loop() {
if (!RTC.read()) {
Serial.println("Read date error: is time set?");
}
else {
Serial.print("Time: ");
Serial.print(RTC.getYear());
Serial.print("-");
Serial.print(RTC.getMonth());
Serial.print("-");
Serial.print(RTC.getMonthDay());
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(RTC.getHour());
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(RTC.getMinute());
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(RTC.getSecond());
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(RTC.getTime());
Serial.println(")");
}
delay(1000);
}