Introduction
PROFINET (Process Field Network) is a network standard for Industrial Automation based on open Ethernet and non-proprietary for automation.
The industrial Raspberry PLC has two Ethernet ports, and its own OS from the Raspberry, Raspbian, Linux.
Let's go to learn how to run the p-net PROFINET device stack and its sample application on an industrial Raspberry Pi PLC.
Note: Industrial Shields does not provide Profinet libraries to control the Inputs & Outputs. You can use our libraries based on C++, Python or Node-Red that you can find in our official github.
Related Links
Explanation
Requirements
- 1x Raspberry Pi
- 1x Raspberry Pi based PLC
- Ethernet/USB Hub
- Raspberry power cable - USB-C type
- 2x Ethernet cables
PROFINET
PROFINET is the international open Ethernet industrial standard of PROFIBUS & PROFINET (pi) for automation.
- PROFINET uses the TCP/IP and LO standards, is PROFI real-time Ethernet, and allows investment protection with the integration of fieldbus systems.
- ProFiNet IO (Input Output): Developed real-time (RT) and real-time isochronous (IRT) communication with the decentralized periphery. The names RT and IRT are limited to describing the properties in time for communication in ProFiNet IO.
The PROFINET concept offers modular mode structure so that users can select cascade connection themselves. They differ essentially due to the type of data exchange to meet the requirements, partly very high speed.
With PROFINET, communication without discontinuities from the management level to the field level is possible. On the other hand, it meets the great demands imposed by industry, e.g., ex. wiring and connection system suitable for industrial environment, real time, motion control in isochronous mode, non-proprietary engineering, etc.
PROFINET was developed with the aim of fostering a process of convergence between industrial automation and the information management platform for corporate management and global corporate networks. It applies to Ethernet-based distributed automation systems that integrate existing field bus systems, for example PROFIBUS, but without modifying them.
Notes to advanced users
The IO-device sample application can be running on:
- Raspberry Pi
- Any Linux OS
- An embedded board running an RTOS, such as RT-kernel
Files
The sample_app directory in the p-net repository contains the source code for this tutorial. It also contains a GSD file which tells the IO-controller how to communicate with the IO-device. Those parts of the sample application that are dependent on whether you run Linux or an RTOS are located in src/ports.
Install dependencies
See how >>
2. Then, in order to compile p-net on Raspberry Pi, you need a recent version of cmake. Install it:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install snapd
sudo reboot
sudo snap install cmake --classic
cmake --version
Download and compile p-net
sudo apt install git
2. Create a directory called profinet:
mkdir /home/pi/profinet cd /home/pi/profinet
3. Clone the repository with submodules. Then create and configure the build:
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/rtlabs-com/p-net.git cmake -B build -S p-net cmake --build build --target install
Notes to advanced users
If you have already cloned the repository without the --recurse-submodules flag, then run in the p-net folder.
git submodule update --init --recursive.
Alternate cmake command to also adjust some settings:
cmake -B build -S p-net -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug -DBUILD_TESTING=OFF -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON -DUSE_SCHED_FIFO=ON
Depending on how you installed cmake, you might need to run snap run cmake instead of cmake.
Run the sample application
1. Go to the /home/pi/profinet/build directory:
cd /home/pi/profinet/build
sudo ifconfig eth0 192.168.0.50 netmask 255.255.255.0 up
sudo ./pn_dev -v -v -v -v
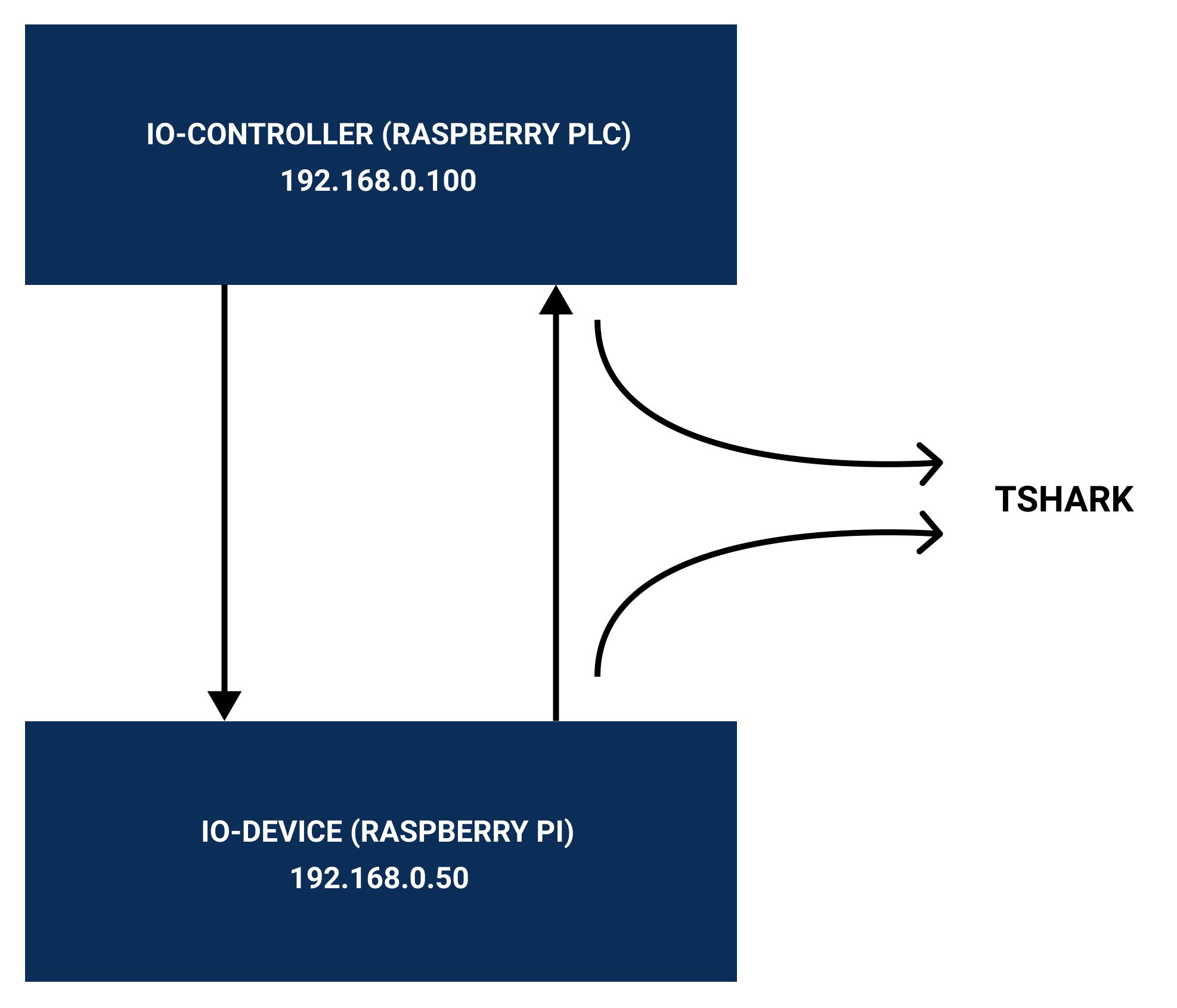
From the Raspberry PLC
1. Configure the Ethernet interface from the Raspberry Pi industrial PLC and set the initial IP address:
sudo ifconfig eth0 192.168.0.100 netmask 255.255.255.0 up
sudo apt update sudo apt install -y tshark
sudo groupadd tshark
sudo usermod -a -G tshark $USER
tshark --version
sudo tshark
tshark -D
sudo tshark -i eth0
Get the results
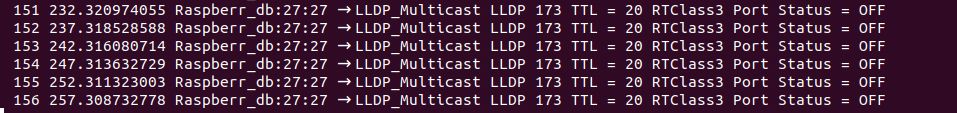

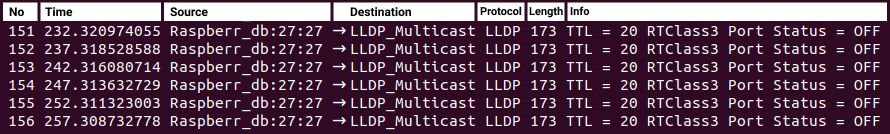
LLDP
LLDP or Link Layer Discovery Protocol is used by PROFINET to determine and manage neighborhood relationships between PROFINET devices. LLDP uses the special multicast MAC address: 01-80-C2-00-00-0E and the Link layer Ethernet II and IEEE 802. 1Q and Ethertype 0x88CC (PROFINET). Finally, the port number is non relevant:
Autostart on boot
· If you want pnet to run when the Pi is turned on, or re-booted, first enable the serial port console by writing the line
enable_uart=1
in the file /boot/config.txt
1. Go to /etc/dhcpcd.conf and include these lines to set a static IP:
interface eth0 static ip_address=192.168.0.100/24
2. Then, you can enable the service to autostart by running the following commands:
sudo cp /home/pi/profinet/p-net/src/ports/linux/pnet-sampleapp.service /lib/systemd/system
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable pnet-sampleapp.service
Start service
sudo systemctl start pnet-sampleapp.service
· To see the status of the process, and the log output:
sudo systemctl status pnet-sampleapp.service
journalctl -fu pnet-sampleapp
Finally, reboot to apply the changes and get your service running!
PROFINET & Raspberry PLC tutorial: How to set communication on Linux