Index
1. Introduction
2. Requirements
3. Description
4. Characteristics
5. How it works
6. Connections
7. Software
Introduction
The Sharp GP2Y0A02YK0F is an optical distance sensor. It consists of an infrared LED together with a position detector device (PSD) and an integrated processor responsible for calculating the distance.
The sensor continuously scans the objects located in front of it and provides the output through an analog voltage reference, so we can use the Arduino analog inputs to read the value of the distance.
The measuring range is from 20 to 150 cm, maintaining a high degree of precision throughout the interval. The supply voltage is 4.5 to 5.5V and the current consumption is 33mA. The refresh interval between measurements is about 80ms.
The GP2Y0A02YK0F is a simple device to connect and use. However, it must be taken into account that it incorporates a JST (Japanese Solderless Terminal) connector for its connection, so we will have to use a connector of this type or directly solder the terminals on the board.
Requirements
Ethernet PLC or 20 I/Os PLC:
GP2Y0A02YK0F optical distance sensor:
GP2Y0A02YK0F Datasheet >>>
Industrial Shields boards:
Use the mapping pins of IS boards >>>
Description
GP2Y0A02YK0F optical distance sensor:
- Outline dimensions: (measure unit: mm)
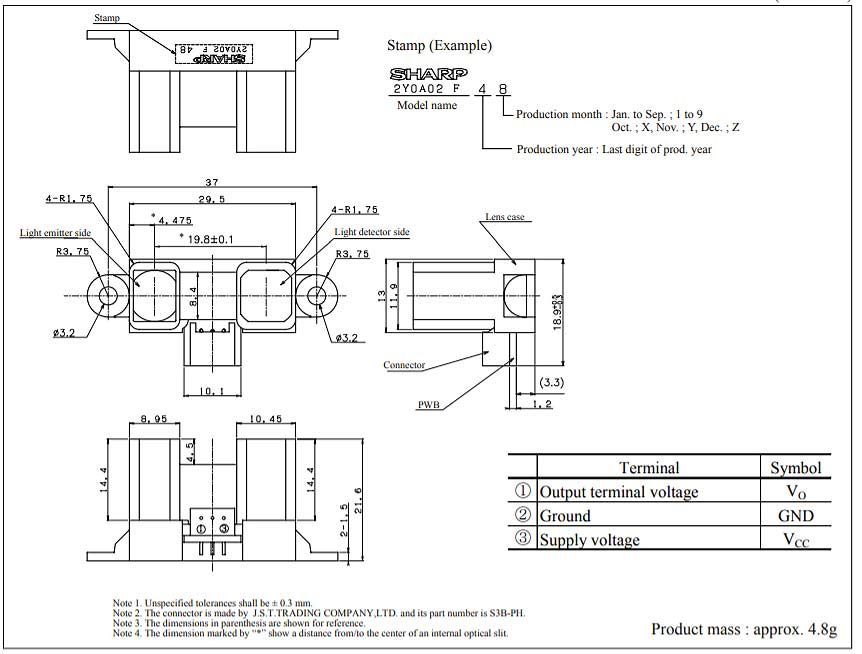
| Characteristics | |||||||||||
| Supply voltage (Vcc) | (-0.3 to 7) V | ||||||||||
| Output terminal voltage (Vo) | (-0.3 to Vcc+ 0.3) V | ||||||||||
| Operating temperature (Topr) | (-10 to +60) ºC | ||||||||||
| Storage temperature (Tstg) | (-40 to +70) ºC | ||||||||||
| Average supply current (Icc) | typ. 30mA, max. 50mA | ||||||||||
| Measuring distance range (ΔL) | (20 to150) cm | ||||||||||
| Output Voltage (V0) | (mín. 0.25 ; typ. 0,4 ; max. 0,55) V | ||||||||||
How it works
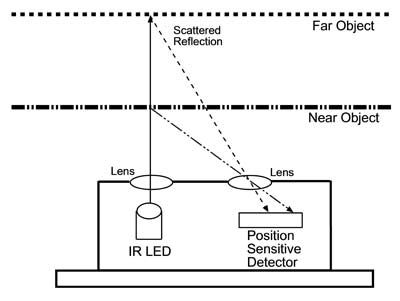
The infrared LED emitter emits a beam of infrared pulsed light with a wavelength of 850nm +/- 70nm. Pulsed light is sent to minimize the influence of the ambient light and the color of the object in the measurement.
The position detector PSD (position sensitive detection) is actually a small linear CCD sensor that receives light reflected on any object in the path of the beam. The sensor uses triangulation to determine the distance of the sensor to objects located in front of the beam.
The Sharp sensor is more accurate than ultrasound sensors such as the HC-SR04, especially in medium and long distances, where ultrasound sensors are affected by the rebounds and echoes produced by the geometries of the environment.
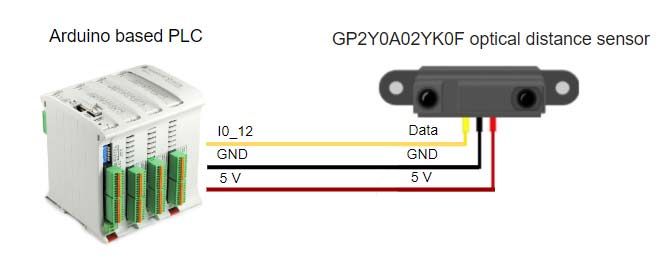
Connections
Pin 1 (Data) --> I0_12
Pin2 (Gnd) --> Gnd
Pin3 (5V) --> 5V
Final Connection:
Software
This simple sketch allows us to perform analog readings of the GP2Y0A02YK every sec. For this, we have used entry I0.12 of our M-Duino. You can use any of the analog inputs available on your Arduino based PLC.
As a test we will check the result monitored by the serial port checking the analog Value readed, the voltage received and finally the distance between the sensor and the object.
const long referenceMv = 5000;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
//lectura de la tensión
int val = analogRead(I0_12);
int mV = (val * referenceMv) / 1023;
int cm = getDistance(mV);
//mostrar valores por pantalla
Serial.print(mV);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.println(cm);
delay(1000);
}
//interpolación de la distancia a intervalos de 250mV
const int TABLE_ENTRIES = 12;
const int INTERVAL = 250;
static int distance[TABLE_ENTRIES] = {150,140,130,100,60,50,40,35,30,25,20,15};
int getDistance(int mV) {
if (mV > INTERVAL * TABLE_ENTRIES - 1) return distance[TABLE_ENTRIES - 1];
else {
int index = mV / INTERVAL;
float frac = (mV % 250) / (float)INTERVAL;
return distance[index] - ((distance[index] - distance[index + 1]) * frac);
}
}

Measuring distances using an optical distance sensor