Introduction
While we work in industrial environments, data often have to be synchronized in order to keep it updated at all times.
In this post, we will learn to use the Rsynctool, with which you can synchronize all your local and remote data to any PLC! We are going to use an industrial Raspberry PLC.
Latest Posts
Rsync
In these blogs posts, we show you how to send files between a Raspberry Pi based PLC and your computer, Windows or Linux:
- How to use SCP to transfer files between Linux and Raspberry PLC >>
- How to transfer files between Raspberry Pi PLC and your computer >>
- Rsync o 'remote sync' is a fast and extraordinarily versatile file copying tool. It can copy locally, to/from another host over any remote shell, or to/from a remote rsync daemon.
- It offers numerous options that control every aspect of its behavior and permit very flexible specifications of the set of files to be copied.
- Furthermore, it is famous for its delta-transfer algorithm, which reduces the amount of data sent over the network by sending only the differences between the source files and the existing files in the destination.
- Rsync is widely used for backups and mirroring, and as an improved copy command for everyday use.
Synopsis
The synopsis, like cp, scp or ssh, is the same:

IP addresses
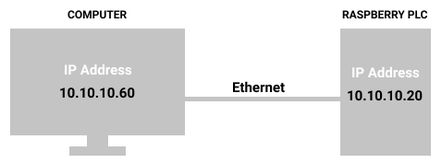
These are the IP addresses of our devices.
On the one hand, our laptop based on Linux has the IP address: 10.10.10.60 for the Ethernet interface.
On the other hand, the industrial Raspberry Pi PLC has the IP address: 10.10.10.20 for the Ethernet interface.
From local to remote
Based on this, we are going to do the following:
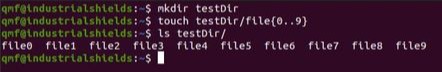
1. We will create a local folder with 10 files on our laptop called testDir.
mkdir testDirtouch testDir/file{0..9}ls testDir/
With the ls command, we will list the files in the folder and check that they have been created correctly.
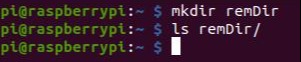
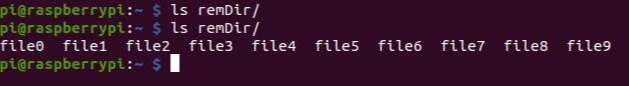
2. We will create a folder in the Raspberry PLC called remDir, to be able to send files from local to remote. With the ls command, we will list the files and check that it is empty:
mkdir remDir
ls remDir
3. Now, in order to sync the data from local to the remote directory, we will execute the following command:
rsync -a testDir/ [email protected]:/home/pi/remDir
The -a option is the archive mode. Equals -rlptoD:
-r --recursive: recourse into directories
-l --links: Copy symlinks as symlinks
-p --perms: Preserve permissions
-t --times: Preserve modification times
-o --owner: Preserve owner (super-user only)
-D: Preserve device files (super-user only) and special files.
From remote to local
1. Let's create a new directory in our computer, called newDir:
mkdir newDir
ls newDir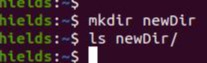
2. Now, we are going to rsync from the remote host to the localhost.
rsync -a [email protected]:/home/pi/remDir/ newDir/
In this step, we are going to emphasize the / mark next to the remDir. In this example, we will see the difference.
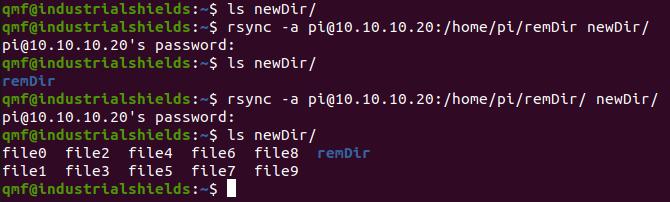
Test
Now, type the following command:
man rsync
And discover all the options available in rsync command for you to optimize your file copies!


How to sync local and remote directories with Raspberry PLC