Index
Introduction
In this post, we are going to work with lights using the DMX512 Industrial Shields Library. With this library, we can work easily with the DMX protocol and work up to 512 different channels.
The DMX512 (Known as DMX) protocol is used in professional lighting systems and smoke or special effects machines.
Thanks to this communication, we can send to each of the 512 addresses a number between 0 and 255. Using this control, and knowing that some systems could have more than one address, we can work with a wide range of systems.
Previous readings
We recommend you to read the following blogs in order to understand the program of this blog. We used the following blog posts in order to do this example:
Know how to program our industrial PLC controller for industrial automation with Arduino IDE: Installing the Industrial Shields's boards in the Arduino ID
Requirements
In order to work with a DMX512 protocol, you will need the next following things:
Any of our industrial controllers:
DMX512 decoder
Connecting the DMX512 decoder to the industrial controller Arduino
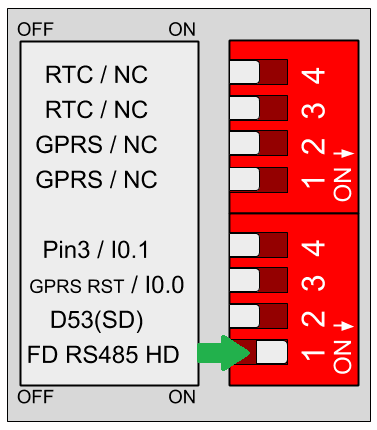
1) The first thing we must do is connect the RS485 bus to the decoder. We must keep in mind to put in the correct position the RS485 switch:
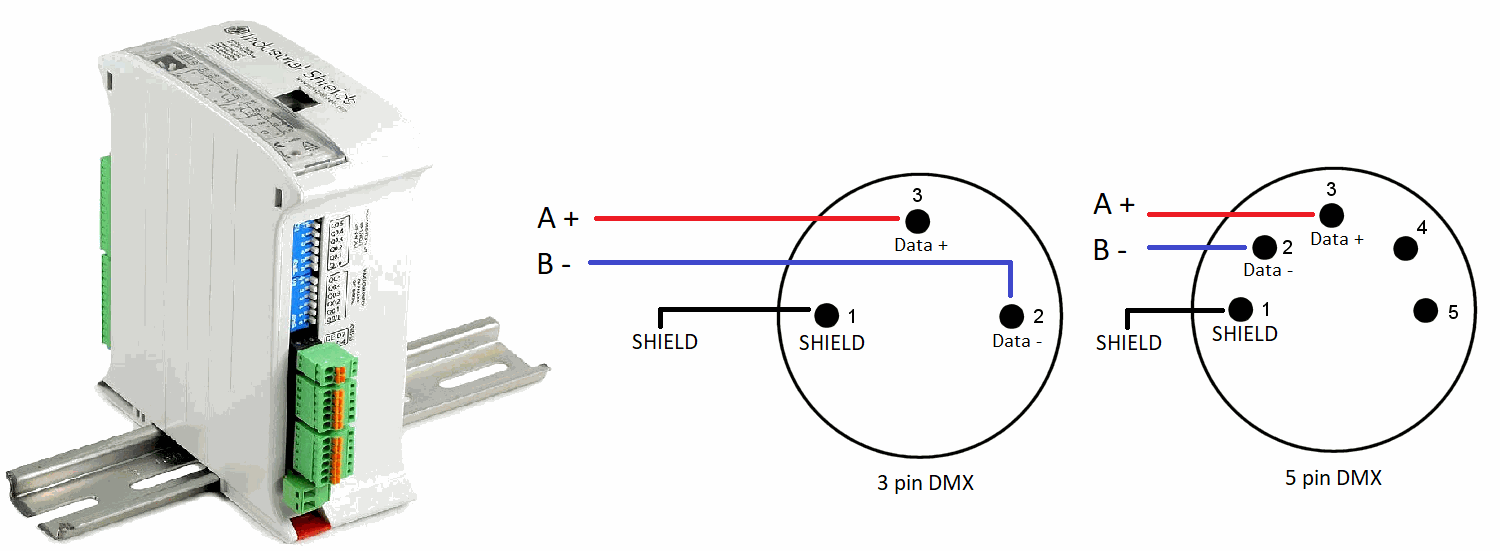
2) Once the Programmable Logic Controller is correctly configured, we must connect the pins to the DMX encoder:
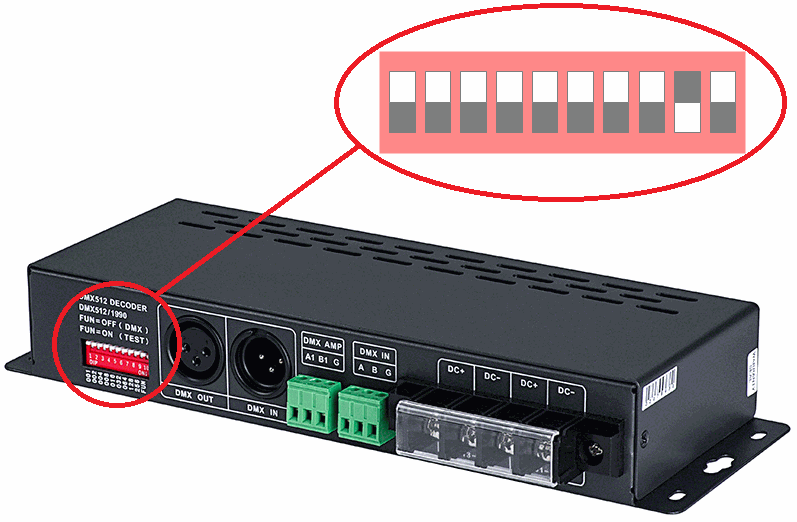
Remember to configure each DMX encoder with the correct address. Usually, there is a switch in the decoder. This configuration will be important because with that we will be able to set the address range will have this encoder:
Software
1) The first thing we must do is include the Arduino library that includes the DMX512 functions:
#include <DMX512.h>Remember to initialize the DMX library:
DMX512.begin();
DMX512.begin();2) Before sending anything through this library, we will need to ask if the bus is free. The next function returns TRUE if the bus is idle. FALSE if is still working:
DMX512.idle();
DMX512.idle();3) Finally, with the next function, we will be able to send information to the DMX addresses. Keep in mind this function need a pointer to a variable uint8_t with the power level (channels), and a variable const uint16_t with the number of total channels (numChannels):
DMX512.write(*channels, numChannels);
DMX512.write(*channels, numChannels);Example
The example below sends information to the DMX addresses 1, 2 and 3. If we put a DMX encoder working with these addresses, we will see a light blinking slowly:
// DMX512 library example // by Industrial Shields
// Include the DMX512 library #include <DMX512.h>
// Define the variables for work with the addresses uint8_t channels[] = {0, 80, 160}; const uint16_t numChannels = sizeof(channels) / sizeof(uint8_t); // Setup function void setup()
{DMX512.begin(); } // Loop function void loop()// Ask if the DMX bus is busy
{if (DMX512.idle()){// Wait some time between commandsdelay(100);// Update channels brightnessfor (uint16_t i = 0; i < numChannels; ++i){// Increase the power value of the channelschannels[i] += 5;} // Update channels DMX512.write(channels, numChannels); } }
DMX512 on a Industrial Shields'® PLC Arduino