Index
1. Introduction
2. Previous reading
3. Requirements
4. Configuring the switches
5. Output types
6. Hardware
7. Software
8. Example
9. Basics: Analog outputs in Arduino PLC
Introduction
In this post, we are going to explain how to do the basics in order to work with analog outputs of Industrial Shields' programmable logic controllers. Reading this post, you will be able to understand how to connect and configure the analog outputs of your industrial Arduino Controller.
Previous readings
We recommend you to read the following blogs in order to understand the program of this blog. We used the following blog posts to do this example:
How to program our industrial PLC with Arduino IDE: Install Industrial Shields's boards in the Arduino ID.
Requirements
In order to work with analog outputs you will need any of our industrial controllers for industrial automation:
Configuring the switches
Most of the analog outputs are always connected to the internal Arduino, but in a few cases, the user can choose between a special peripheral configuration or a GPIO by changing the position of the Dip Switches.
Each switch can select only one configuration. For example, in this case, we are watching the GPIOs configuration o an M-Duino 21+. If we put the switch to the right position (ON) in the lower one, the output Q0.0 will be activated and we will be able to work this as digital. If the switch is in the left position (OFF) we will activate the output as analog. Keep in mind each switch has two different configurations: you must select the right (ON) or the left (OFF) option.
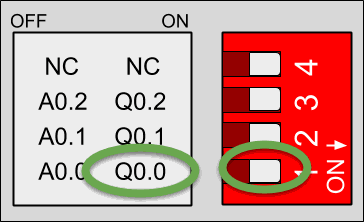
Q0.0 enabled - A0.0 disabled
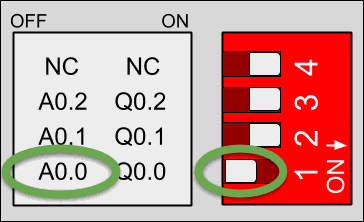
Q0.0 disabled - A0.0 enabled
Output types
In all of the Industrial Shields' Arduino based PLCs, analog outputs can work at:
0V - 10V analog output
Analog outputs have a special draw in the case of the PLC:
Analog output Serigraphy
Hardware
The following image shows how to connect an analog output to the PLC:
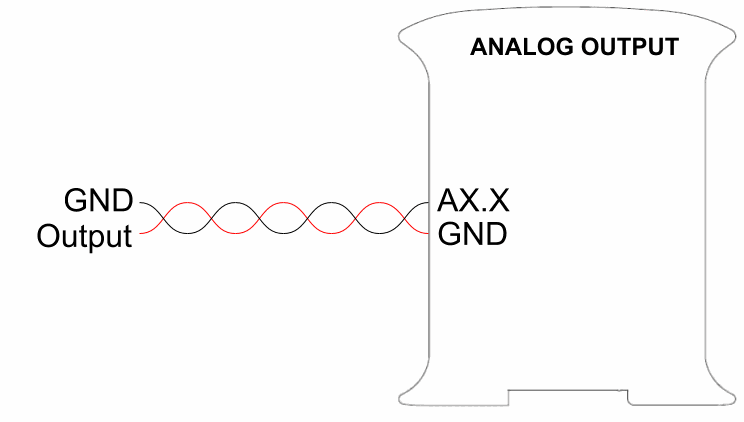
0Vdc -10Vdc Analog output
Software
In order to program the analog outputs, we must keep in mind that we can write the values with the following command:
analogWrite(GPIO,value);This function puts the value of the analog output "A0.0" to 255 (meaning 10V):
analogWrite(A0_0,255);Example
You can see a write analog GPIO in the following paragraph:
// Analog write example// Set the speed of the serial port
// This example writes the A0_0 and shows via serial the value
// Setup function
void setup()
{Serial.begin(9600UL);
pinMode(A0_0,OUTPUT); // Only required in ESP32 based PLCs}Serial.println("Value: 0");
// Loop function
void loop()
{
analogWrite(A0_0, 0);
delay(1000);
Serial.println("Value: 100");
analogWrite(A0_0,100);
delay(1000);
Serial.println("Value: 255");
analogWrite(A0_0,255);
delay(1000);}
Basics about analog outputs of an industrial PLC