INTRODUCTION
The Read Input Registers Modbus RTU function (Modbus Function Code: 4), is used for reading from 1 to 125 contiguous input registers in a remote device.
In this blog post, we will be reading input registers between Arduino based PLC set as client - server >
MODBUS RTU
To know more about Modbus RTU and how the library works, please visit the following blog post:
HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS
- 2x M-Duino PLC >
- Power Supply >
- B type cable , to program the Arduino based PLC
- Two twisted pair cables, for RS485.
SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS
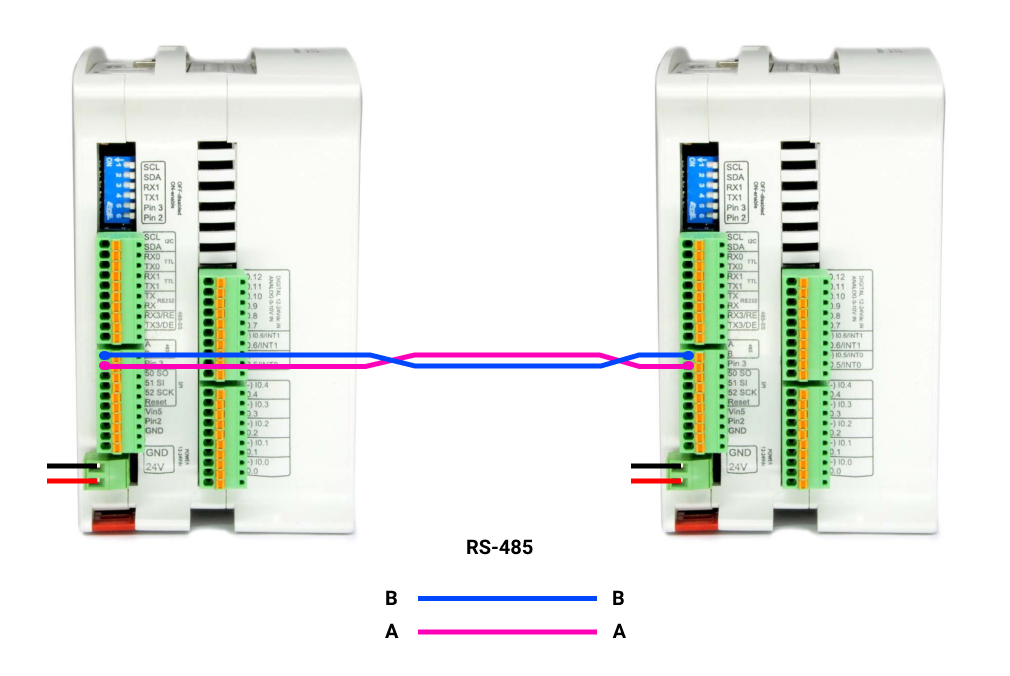
CONNECTIONS
Now, in order to set a Modbus RTU communication, we are going to do the following:
1. Power the PLC between 12 and 24V.
2. Wire the cables through RS-485. This is based on a twisted pair cables, on cable from A+ to A+, and the other one from B- to B-.
3. Set the red switch to the Half-Duplex: HD
MODBUS RTU MASTER READ INPUT REGISTERS
In order to set an M-Duino as a master and the other one as a slave, we will have to program both to execute each code. So, in order to program the master, open up a new file of Arduino IDE, and paste the code below:
/*//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void loop() { // Send a request every 1000ms if (millis() - lastSentTime > 1000) { // Send a Read Input Register request to the slave with address 31 // It requests for 1 register starting at address 0 // IMPORTANT: all read and write functions start a Modbus transmission, but they are not // blocking, so you can continue the program while the Modbus functions work. To check for // available responses, call master.available() function often. if (!master.readInputRegisters(31, 0, 1)) { // Failure treatment } lastSentTime = millis(); } // Check available responses often if (master.isWaitingResponse()) { ModbusResponse response = master.available(); if (response) { if (response.hasError()) { // Response failure treatment. You can use response.getErrorCode() // to get the error code. } else { // Get the register value from the response uint32_t reg = response.getRegister(0); Serial.print("Reg: "); Serial.println(reg); } } } }
Copyright (c) 2018 Boot&Work Corp., S.L. All rights reserved This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as
published by
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version. This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU Lesser General Public License for more details. You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
*/ #include <ModbusRTUMaster.h> // Define the ModbusRTUMaster object,
using the RS-485 or RS-232 port (depending on availability)
#if defined HAVE_RS485_HARD
#include <RS485.h>
ModbusRTUMaster master(RS485); #elif defined HAVE_RS232_HARD
#include <RS232.h>
ModbusRTUMaster master(RS232); #else
ModbusRTUMaster master(Serial1);
#endif uint32_t lastSentTime = 0UL;
const uint32_t baudrate = 38400UL;
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600UL); // Start the serial port
#if defined HAVE_RS485_HARD
RS485.begin(baudrate, HALFDUPLEX, SERIAL_8E1);
#elif defined HAVE_RS232_HARD
RS232.begin(baudrate, SERIAL_8E1);
#else
Serial1.begin(baudrate, SERIAL_8E1);
#endif // Start the modbus master object.
// It is possible to define the port rate (default: 19200)
master.begin(baudrate);
}
1. Once you pasted the sketch, click on Tools > Board > Industrial Shields boards > And select the M-Duino family.
2. Then, select the PLC model by going to Tools > Model > And selecting the model. In our case: M-Duino 21+
3. Select the port by going to Tools > Port > And select the port of the Arduino board.
4. Finally, either click on the arrow to upload the sketch, or go to Sketch > Upload.
MODBUS RTU SLAVE
Once the master is already programmed, we are going to do the same as with the Master PLC, but choosing the ModbusRTUSlave sketch. So:
1. Change the B type cable and connect it to the other M-Duino PLC.
2. Go to the top bar, and click on: File > Examples > Modbus > and select the ModbusRTUSlave sketch.
3. Once the sketch is opened, click on Tools > Board > Industrial Shields boards > And select the M-Duino family.
4. Then, select the PLC model by going to Tools > Model > And selecting the model. In our case: M-Duino 21+
5. Select the port by going to Tools > Port > And select the port of the Arduino board.
6. Finally, either click on the arrow to upload the sketch, or go to Sketch > Upload.
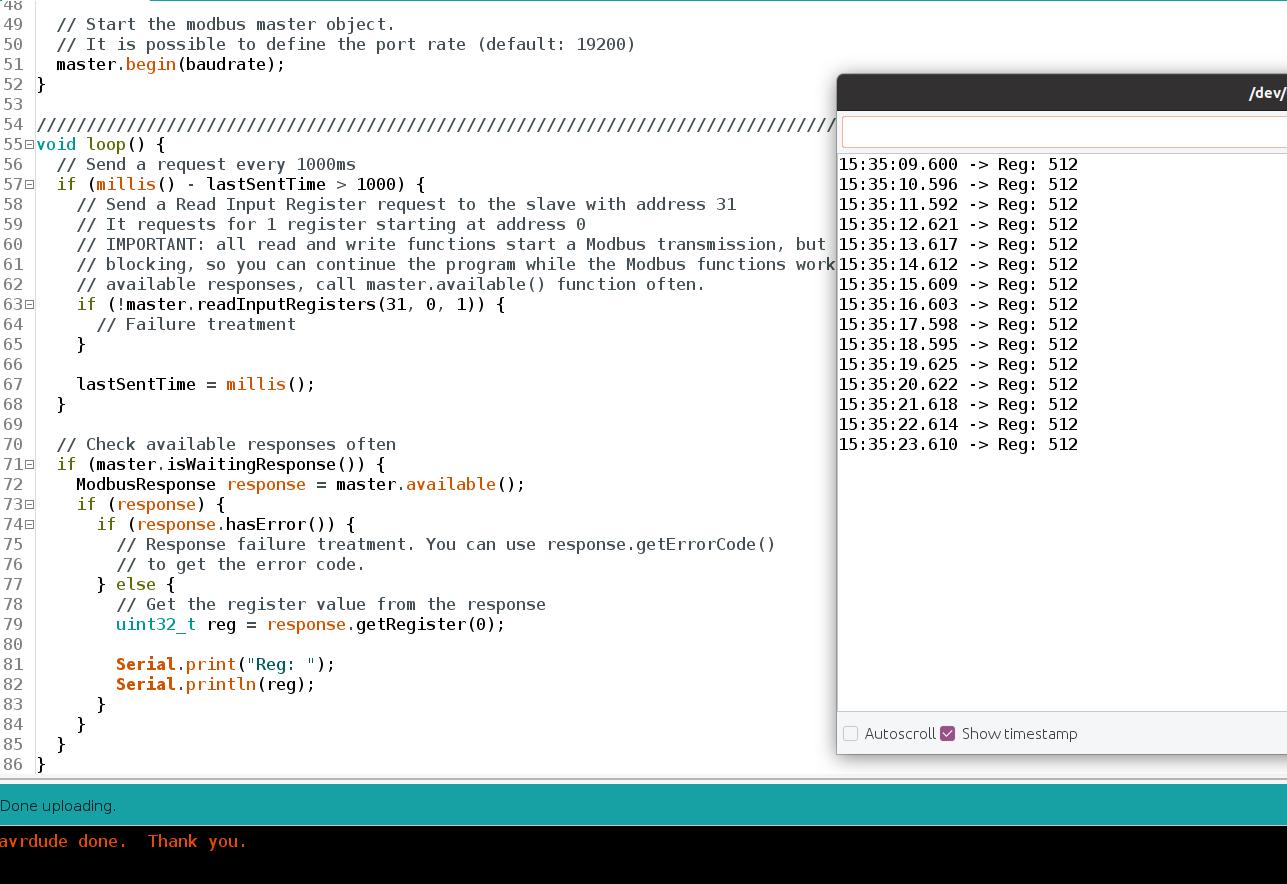
TIP: We are wiring a cable from the 5V of the M-Duino Slave PLC to its I0.7 analog input, to add some voltage to the input and get a result different from 0.
Now, open the serial monitor from the master, and read the first register of the slave PLC!
Modbus RTU Tutorial: How to Read Input Registers with M-Duino PLC